Battery Basics
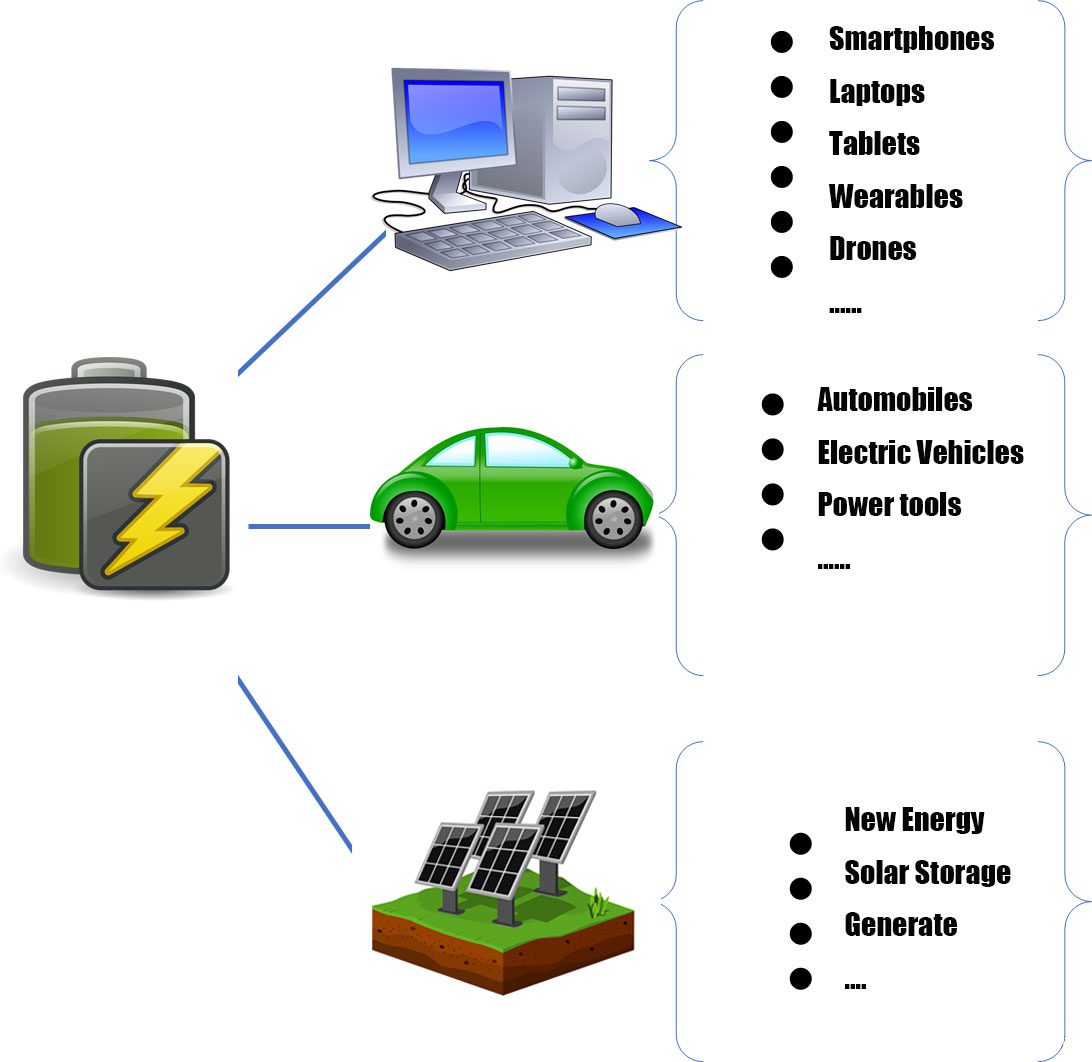
Batteries are now heavily used in our lives, mainly in 3C consumer, power, and energy storage.
WELCOME FOLLOW US TO GET MORE POWERFUL BATTERY
Battery Principles
In a battery, there is a positive electrode (positive electrode) and a negative electrode (negative electrode), which are made of metal,
and a substance that conducts electricity by means of ions (electrolyte) is filled between the positive and negative electrodes. The
metal electrode is melted by the electrolyte and divided into ions and electrons, which move from the negative electrode to the
positive electrode to produce an electric current. In a secondary battery, electrons are stored in the negative terminal by charging
the battery before it is used, and when the battery is used, the stored electrons move to the positive terminal to produce electricity.
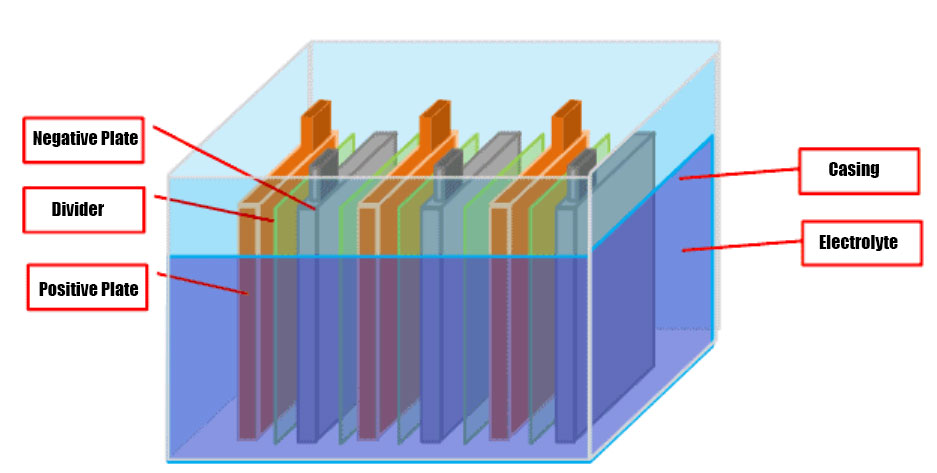
Battery composition
Positive electrode: lithium composite material + conductive agent + binder + collector
Negative electrode: graphite + conductive agent + binder + collector
Electrolyte: made of organic solvent, electrolyte, additives under certain conditions, configured according to a certain ratio, is the channel
for positive and negative electrode ion transmission
Diaphragm: single-layer PE + ceramic & polymer
Battery Category
Batteries can be divided into: lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries, graphene batteries, solid-state batteries, etc. according to the material
composition of different materials.Graphene batteries, solid-state batteries and so on.
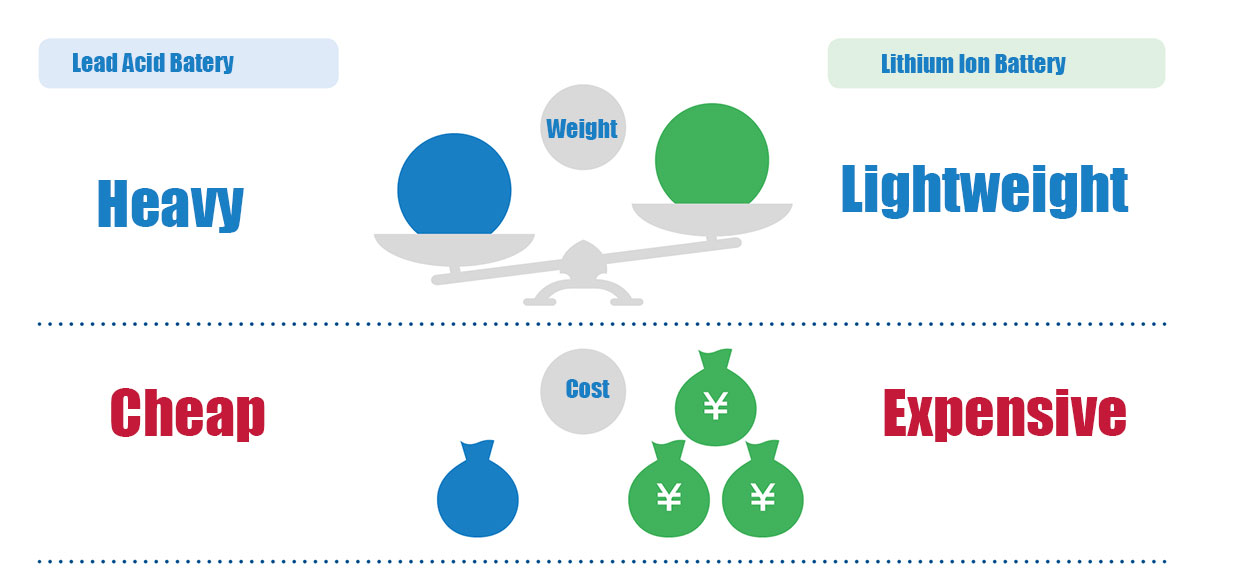
Lead batteries have a long history of being used more than 100 years ago, and continue to be used as batteries for some automobiles and
battery cars even now that new types of batteries such as lithium-ion batteries have been developed. Lead batteries use lead for both the
positive and negative electrode materials, making them very inexpensive to manufacture compared to lithium-ion batteries. However,
since lead is heavier than other metals, the battery itself is heavier. In addition, the maximum voltage is only 2V, and the self-discharge is
also a disadvantage of the lead battery. Although lead batteries have these disadvantages, but because it is cheap, and the technology is
basically mature, high reliability, still has a good application value.
Lead-acid battery is a kind of battery whose electrodes are mainly made of lead and its oxides, and whose electrolyte is a sulfuric acid
solution. Lead-acid battery discharge state, the main component of the positive electrode is lead dioxide, the main component of the
negative electrode is lead; charging state, the main component of the positive and negative electrodes are lead sulfate.
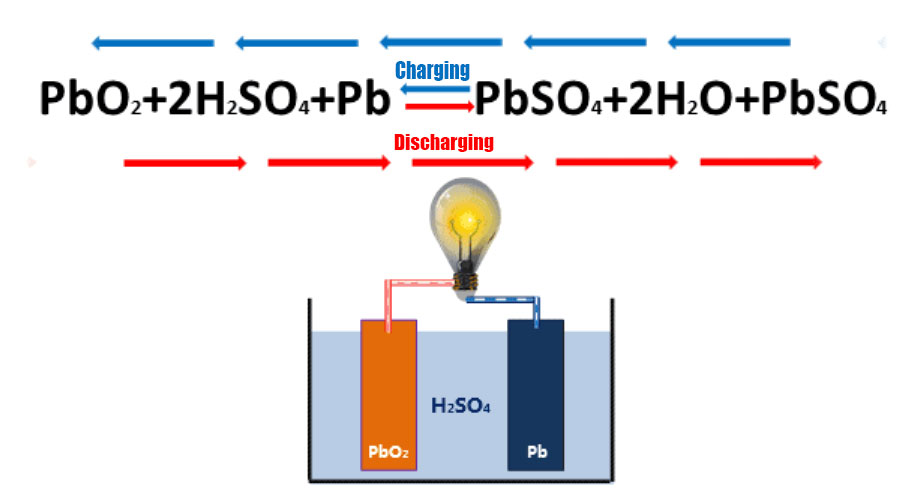
(Discharge chemical reaction:The positive active substance (lead dioxide) in a lead-acid battery reacts with the negative active substance
(lead sponge) and the electrolyte (30%-40% dilute sulphuric acid solution) to form lead sulphate and water.
Charging chemical reaction Lead sulfate and water are converted to lead dioxide, lead sponge and dilute sulfuric acid.)
Tips: Lead-acid batteries because the electrolyte is directly involved in the redox reaction, the electrolyte will exist a large consumption
leading to a decline in battery capacity or early failure, so lead-acid batteries need to replenish the electrolyte in a timely manner.
lithium ion battery
Lithium-ion batteries use a lithium-containing metal compound for the positive electrode and carbon (graphite), which absorbs lithium,
for the negative electrode. With this structure, power can be generated without melting the electrodes with electrolyte as in conventional
batteries, thus slowing down the aging of the battery itself and enabling it to not only store more power, but also increase the number of
times it can be charged and discharged. In addition, lithium is a very small and lightweight material, which enables the battery to be
compact and lightweight, among other advantages.
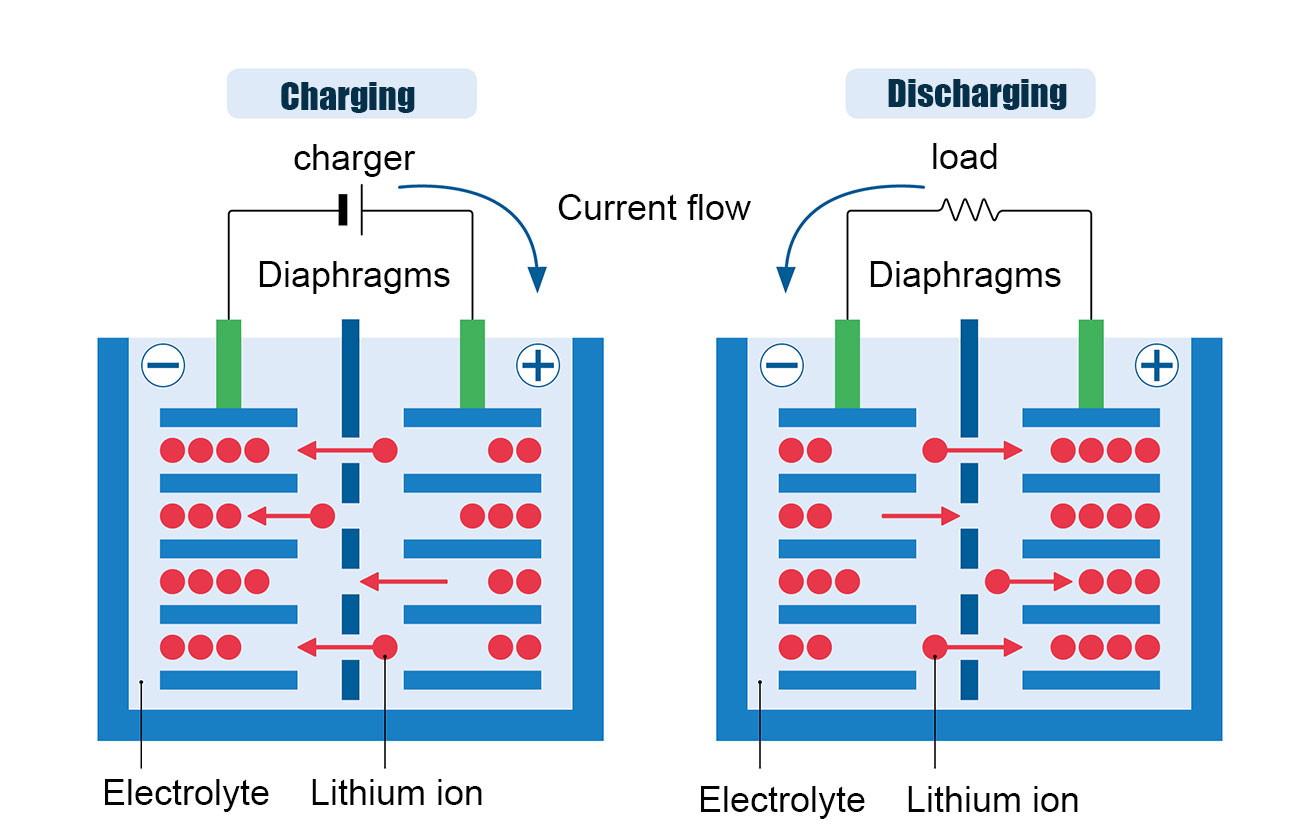
Charging process: Li atoms at the positive electrode break down into Li+ ions + electrons, the Li+ ions reach the negative electrode through
the electrolyte and the electrons reach the negative electrode through an external circuit (de-embedding). At the negative electrode,
Li+ ions and electrons combine to form Li atoms (insertion).
Discharge process: Li atoms at the negative electrode decompose into Li + ions + electrons, Li + ions through the electrolyte to reach the
positive electrode, electrons through the external circuit to reach the positive electrode (de-insertion). At the positive electrode Li+ ions
+ electrons combine to form Li atoms (embedded).
Lithium Battery Classification
| Cobalt-based lithium ion battery | 3.7V | 500-1000times | The cathode uses lithium cobaltate. Lithium cobalt is relatively easy to synthesise and easy to use, and thus the first lithium-ion batteries to be mass-produced were lithium cobalt-ion batteries. However, because cobalt is a rare and expensive metal, it is hardly ever used in automotive parts. |
| Manganese lithium ion battery | 3.7V | 300-700times | Lithium manganate is used for the cathode. The advantage is that the voltage performance is similar to that of cobalt-based lithium-ion batteries, and the manufacturing cost is cheap. The disadvantage is that the manganese may melt into the electrolyte during charging and discharging, shortening the life of the battery. |
| Lithium iron phosphate lithium battery | 3.2V | 2000-3000times | Cheap and cycle life (aging from charging and discharging) Calendar life (aging from sitting) Longer voltage than other lithium-ion batteries The advantages of iron phosphate lithium ion batteries are that it is difficult to damage the internal heat structure, high safety, and lower manufacturing costs than manganese batteries due to the use of iron as a raw material. However, the voltage is lower than other lithium ion batteries. |
| Ternary lithium ion battery | 3.6V | 1000-2000times | Ternary lithium-ion batteries are batteries that use cobalt, nickel and manganese in order to reduce the amount of cobalt. Nowadays, most of the ternary lithium-ion batteries have a higher proportion of nickel. Although the voltage is slightly lower than cobalt and manganese, it can reduce the manufacturing cost. However, the synthesis and preparation of each material is difficult, and the stability is low, so there are still problems to be solved as a practical material. |
Graphene battery is actually a single layer of graphite, as long as you can cut a piece out of graphite and that piece has only one layer
of atoms. Graphene battery, is a kind of honeycomb planar film formed by carbon atoms in the form of sp2 hybridisation, is a kind of
quasi-two-dimensional material with the thickness of only one atomic layer, so it is also called monolayer graphite. It is a new energy
battery developed by taking advantage of the characteristics of rapid and massive shuttle movement of lithium ions between graphene
surface and electrodes. Due to the high conductivity, high strength, ultra-light and thin characteristics, graphene in the aerospace
category of the use of the advantages are also extremely prominent.
1, different storage capacity: a lithium battery (subject to the most advanced) specific energy value of 180wh/kg, while a graphene
battery specific energy is more than 600wh/kg.
2, the service life is different: the service life of graphene is twice that of lithium battery, and it is more durable than lithium battery
under high temperature. However, many graphene batteries on the market are actually graphene+battery, not graphene battery in
the real sense. Graphene + battery ≠ graphene battery
What can be seen at present, there are two main directions, one is as a conductive additive, and the other is as a negative electrode
material.
Graphene as a conductive additive can promote fast charging and discharging, but it puts high demands on the process itself.
At room temperature, graphene can't be superconductive either, and doesn't have much of an advantage over cheaper additives.
As for using graphene as a negative electrode material, it theoretically has a higher capacity than graphite electrodes, but the
performance is easily affected by the surface state. Moreover, graphene will meet the challenge of "lifelong enemy" silicon,
after all, silicon as a negative electrode material, the capacity is larger, and more readily available.
A solid state battery is one that uses solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte,

According to the solid electrolyte materials, solid-state batteries can be divided into sulfide, oxide, polymer three systems,
different electrolyte materials have their own advantages and disadvantages, but most of the domestic manufacturers of
solid-state batteries to go to the oxide route, the advantage of the electrolyte chemical stability is high!
Thanks for watching, we're getting better again.
14 Symptoms of Battery management system Failure
Everything About Lead acid Battery,lithium ion b
Share the parts needed by customers to replace t